Abstract
This study aimed to evaluate the use of ferronickel slag (FNS) as a complementary cementitious material in producing Portland cement. The cements were produced containing clinker, gypsum and FNS at 10%, 20% and 30% mass replacement levels, with a reference sample containing 20% limestone filler. The materials were ground and characterized using laser granulometry, specific mass, Blaine specific surface area, fineness, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and X-ray fluorescence (XRF) tests. The gypsum content in the cements was determined by isothermal conduction calorimetry. To analyze the properties of the cements produced, called FNS-10, FNS-20, FNS-30, LF-20, physical, chemical and mechanical characterization was carried out, and the R3 test, standardized by C1897 (2020). The results of the cement tests were compared with the requirements of NBR 16697 (2018) “Portland Cement – Requirements”. In general, it was found that cements composed of FNS, at the three incorporation levels, presented values within the standard requirements, enabling the use of FNS in the production of Portland cements.
Keywords
Ferronickel slag; Supplementary cementitious material; Cement; Portland cement requirements

 Analysis of the incorporation of ferronickel slag for the production of composite Portland cements
Analysis of the incorporation of ferronickel slag for the production of composite Portland cements Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail








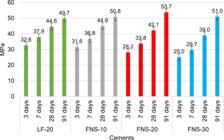
 Source:
Source: 


